| back to: Chapter 1 
Birth of Venus
Sandro Botticelli
oil on canvas
1482 (Italian Renaissance)
 Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow
by Piet Mondrian
oil on canvas
1930 (De Stijl)
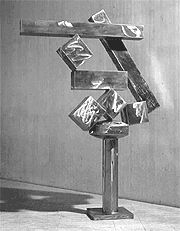
Cubi XVIII
David Smith
polished stainless steel
1964 (Modernist)

Guggenheim Museum
Frank Gehry
1997
architecture (Postmodern)

Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
by Pablo Picasso
oil on canvas
1907 (Cubism)
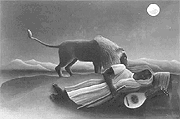
Sleeping Gypsy
Henri Rousseau
oil on canvas
1897 (Outsider, naive)

Haystack at Sunset Near Giverny
Clause Monet
oil on canvas
1891 (Impressionism)

The Night Cafe
by Vincent Van Gogh
oil on canvas
1888 (Post Impressionism)

Object
Meret Oppenheim
fur-covered cup, saucer, and spoon
1936 (Modern)

Apollo and Daphne
Gianlorenzo Bernini
marble sculpture
1622-24 (Baroque)
|
Chapter 2: Visual Elements of Art
Line
Shape, Volume and Mass
- SHAPE
- biomorphic shape: a shape that is naturalistic or organic
- geometric: a shape that is regular and predictable
like this painting by Mondrian
- amorphous: not easily defined as organic or geometric
- form: refers to three-dimensional shapes
This work by David Smith is a good example of a geometric form.
The Guggenheim Museum, Bilbao, Spain, built in 1997 is a great example of organic form.
- volume: is related to amount of space a form uses
- positive and negative shapes: positive indicates filled space and negative indicates empty space. These work together to form figure-ground relationships.
- figure-ground reversals: create optical illusions that contradict our perceptions of positive-negative
- MASS
- actual mass: has measurable volume and weight
- implied mass: the illusion of volume and weight
Light and Value
- VALUE is the relative lightness or darkness of an art element
- CHIAROSCURO is a formula and pattern used to approximate light projected on a three-dimensional surface.
- DESCRIPTIVE AND EXPRESSIVE PROPERTIES OF VALUE is the use of value to create an emotional message in a work of art.

Guernica * Cubism * oil on canvas * 1937 * by Pablo Picasso
Guernica, 1937, oil on canvas, 11'6"x 25'6"
-painting memorializing first saturation bombing of a civilian area
Color
- PSYCHOLOGICAL DIMENSIONS OF COLOR: HUE, VALUE, AND SATURATION
- hue refers to the general colors of the spectrum
- saturation is the pure intensity of a color
- shades are dark values of a color
- tints are light values of a color
- COMPLEMENTARY VERSUS ANALOGOUS COLORS
- complementary colors are colors which are opposite each other on the color wheel and dramatically different in wavelength
A good example of the use of color complements is in the 15th Century painting "The Arnolfini Wedding" by Jan Van Eyck
- primary colors (red, yellow, and blue) are those that cannot be produced by mixing two other colors together
- secondary colors (violet, orange, and green) are those that are produced when two primaries are mixed
- analogous colors are those that are next to each other on the color wheel and share similar wavelenghts
- LOCAL VERSUS OPTICAL COLOR
Texture
- ACTUAL TEXTURE is tactile it is more than visual information
- VISUAL TEXTURE is the illusion of texture
- trompe l'oeil is a method of art that is intended to create a realistic illusion of texture and depth in a work of art. The term means "fool the eye" in French.
- SUBVERSIVE TEXTURE contradicts our past visual experience by using texture in ways that are unexpected. Both Birth of Venus, by Ralph Larmann and Object, by Meret Oppenheim are good examples of this.
Space
- OVERLAPPING
- RELATIVE SIZE AND LINEAR PERSPECTIVE
- ATMOSPHERIC (AERIAL) PERSPECTIVE is a convention of art that was invented by Leonardo da Vinci for creating an illusion of depth by incorporating the natural effects of atmosphere.
Time and Motion
- ACTUAL MOTION is live movement. A work of kinetic art like Alexander Calder's Untitled mobile in the East Wing of the National Gallery of Art in Washington D.C. displays actual motion when we see it in person.
- IMPLIED MOTION AND TIME is a non-moving image that shows movement through the attributes present in the image. Good examples of this are found in Bernini's Apollo and Daphne
- THE ILLUSION OF MOTION is what we experience when we see a movie or series of shapes that note a passage of time. A movie is a series of still frames that do not contain actual motion, but when shown in a time sequence, create an illusion of motion.
Chapter 3
|
|
|

